Before learning about CANDU nuclear reactors, its first important to understand how nuclear energy is used to generate electricity.
What is Nuclear Electricity Generation?
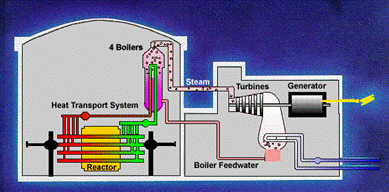
Nuclear electricity generation works by splitting atoms in a process called fission. Uranium-235 is the atom most often used in nuclear reactors and makes up less than 1/100 of natural uranium. When atoms split, they release heat. This heat is used to boil water, which creates steam. The steam is then used to spin turbines connected to generators that produce electricity. Importantly, nuclear reactors produce non-emitting energy, contributing to Canada’s efforts to combat climate change.
What is a CANDU nuclear reactor?
The CANDU reactor, which stands for CANada Deuterium Uranium, is a Canadian innovation that was first developed in the 1960s. Instead of enriched uranium, it uses natural uranium, which doesn’t require extra processing. It also uses heavy water (which has a higher concentration of deuterium oxide or D2O), allowing the reactor to run efficiently with natural uranium.
Another feature is that CANDU reactors can be refueled while still operating, so there is no need to pause electricity generation to refuel. Together, these features make CANDU reactors more flexible, cost-effective, and efficient, especially in places that do not have uranium enrichment facilities.
What is the role of CANDU nuclear reactors in Atlantic Canada?
The Point Lepreau Nuclear Generating Station (PLNGS), near Saint John, New Brunswick, is Atlantic Canada’s only CANDU nuclear generating station. PLNGS has been in commercial operation since 1983, following a long period of operation, and returned to service in 2012. It provides consistent, low-carbon electricity and about 30 per cent of the province’s annual electricity demand, part of the province’s roughly 80 per cent non-emitting supply of electricity. PLNGS is an important economic contributor to New Brunswick as it employees approximately 900 employees and supports local supply chains.
Across Canada, there are several other important CANDU reactors, including:
- Bruce Nuclear Generating Station (Ontario): Canada’s largest nuclear plant, with eight reactors.
- Darlington Nuclear Generating Station (Ontario): four reactors powering Ontario’s grid.
- Pickering Nuclear Generating Station (Ontario): six reactors operating since the 1970s.
What is the role of CANDU nuclear reactors in Atlantic Canada’s net-zero future?
CANDU technology remains a proven, reliable source of clean energy that is supporting regional goals for reducing emissions and maintaining energy security. The future of these reactors in Atlantic Canada centers around the ongoing operation of Point Lepreau Nuclear Generating Station and the potential to deploy new nuclear reactor technologies like Advanced Small Modular Reactors (aSMRs).
SMRs and aSMRs offer promise to the region and Canada as a whole, as smaller, more flexible nuclear options that could complement or succeed current reactor designs. Atlantic Canada is closely watching these developments through companies such as ARC Clean Technology.
Resources:
- https://www.cns-snc.ca/learn-nuclear/basics-of-nuclear/
- https://cna.ca/reactors-and-smrs/how-a-nuclear-reactorworks/
- https://world-nuclear.org/information-library/country-profiles/countries-a-f/canada-nuclear-power
- https://world-nuclear.org/nuclear-essentials
- https://www.nbpower.com/en/about-us/learning/learn-about-electricity/nuclear/
- https://www.cer-rec.gc.ca/en/data-analysis/energy-markets/market-snapshots/2022/market-snapshot-potential-role-nuclear-canada-energy-future.html
- https://www.atlanticaenergy.org/asmrs-101/
- https://www.cns-snc.ca/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/CNS-Point-Lepreau-Licence-Review-Submission-r2.pdf
- https://www.eia.gov/energyexplained/nuclear/

